Popular Articles
Cancertame Ayurvedic Formulation
Carcinoma of Pharynx (Oropharynx, Nasopharynx and Hypopharynx)
Contact Us
Other Articles
2. What is Chemotherapy?
3. What is Radiotherapy?
4. Role of Ayurveda in Cancer Treatment
5. Genesis of Cancer
6. Early Detection of Cancer
7. Diet, Nutrition & Cancer
8. Tobacco Smoking & Cancer
9. Conventional Treatment of Cancer
10. Soft Tissue Sarcoma
11. Mesothelioma
12. Skin Cancer
13. Bone Cancer
14. Leukaemia
15. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL)
16. Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia (CML)
17. Acute Lymphocytic Leukaemia (ALL) & Acute Non-Lymphocytic Leukaemias (ANLL)
18. Acute Myelogenous Leukaemia (AML)
19. Lymphoma
20. Multiple Myeloma
21. Breast Cancer
22. Prostate Cancer
23. Oral Cancer (Carcinoma of the Cheek, Lips & Tongue)
24. Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland
25. Carcinoma of the Paranasal Sinus
26. Carcinoma of Pharynx (Oropharynx, Nasopharynx and Hypopharynx)
27. Carcinoma of the Larynx
28. Brain & Spinal Cord Tumours
29. Primary Tumours of the Brain
30. Metastases in the Brain
31. Carcinoma of the Oesophagus
32. Thyroid Cancer
33. Bronchogenic Carcinoma (Lung Cancer)
34. Secondary Cancers of the Lung
35. Carcinoma of the Stomach
36. Liver Cancer
37. Gallbladder & Biliary Tract Cancer
38. Pancreatic Cancer
39. Kidney Cancer (Renal Cell Carcinoma and Nephroblastoma)
40. Urinary Tract (Transitional Cell Carcinoma) & Bladder Cancer
41. Carcinoma of Colon & Rectum
42. Primary Tumours of the Testis
43. Ovarian Cancer (Stromal, Germ Cell and Krukenberg's Tumour)
44. Carcinoma of Uterus
45. Cervix Cancer
46. Paediatric Cancers
47. AIDS Related Cancers
48. Carcinoma of Unknown Primary Site (CUPS)
49. Role of Nutrition in Cancer Treatment
50. Chinese Medicine in Cancer Treatment
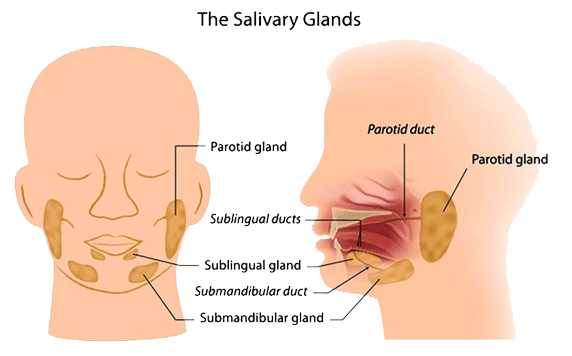
The salivary glands (the glands that secrete saliva) can be divided into two groups, i.e. major salivary glands and minor salivary glands. The major salivary glands include the parotid gland, submandibular gland and the sublingual gland. The minor salivary glands are tiny glands located on the oral mucosa, palate, uvula, floor of the mouth, posterior part of the tongue, retromolar and the peritonsillar areas. Carcinoma may arise from any of the major or the minor salivary glands. The exact cause of salivary gland carcinoma is not fully understood but smoking and exposure to radiotherapy of the head & neck area are considered as the major risk factors.
Carcinoma of the salivary gland usually presents as a slow-growing lump in the cheek along with dull but progressive pain. The tumour is usually fixed to the mandible and the adjacent muscles & the skin leading to restricted movements of the jaw. There may be anaesthesia of the overlying skin or the mucous membrane, resorption of the bone and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck. The parotid gland carcinoma usually presents as a rapidly growing tumour along with progressive facial nerve palsy and neuralgia.
Staging of salivary gland carcinoma is done as follows:
- In stage I of the tumour is less than 4 cm in size.
- In stage II, the tumour is 4 cm to 6 cm in size.
- In stage III, the tumour is more than 6 cm in size; or there is involvement of a single group of lymph nodes on the same side of the neck.
- In stage IV, the tumour is larger than 6 cm in size and invades adjacent tissues; or there is extensive involvement of the lymph nodes, or the tumour metastasises to distant parts of the body.
- Recurrent salivary gland carcinoma is the one that reappears after an apparent recovery in response to the initial treatment.
Procedures used in diagnosis & evaluation of the salivary gland carcinoma include MRI, CT scan and biopsy.
Disclaimer:
This content is for information and educational purposes only and should not be perceived as medical advice. Please consult a certified medical or healthcare professional before making any decision regarding your health using the content above.
Click here to go back to the list of all Articles



Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland